2024-10-05 Linux memory cgroups counters explained
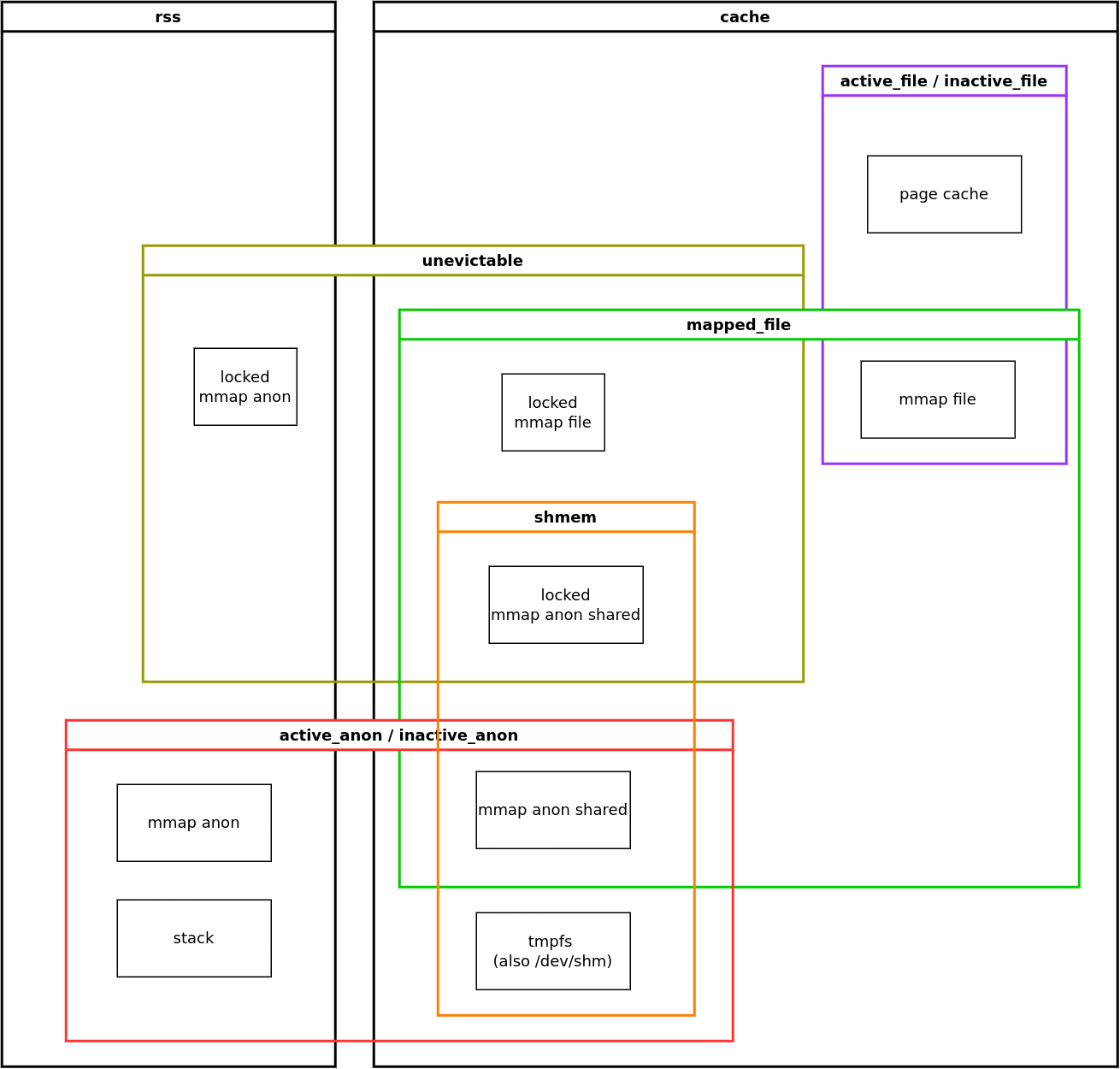
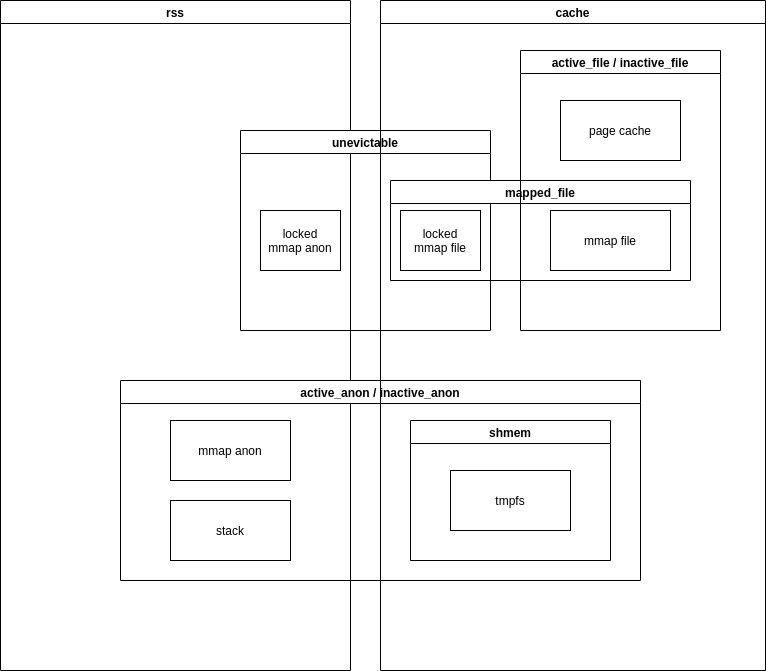
Linux memory cgroup (“memcg”) counters look deceptively simple: a handful of numbers like rss, cache, anon, file, slab, swap, inactive/active, plus a few totals and limits. In practice, these fields are easy to misread, because they don’t form a clean partition of “memory used by this group.” Some counters overlap, some are derived, some represent types of pages while others represent where those pages live (RAM vs swap) or how reclaimable they are.
Here I provide diagrams showing relationships between differnt memory cgroup counters.
Counters considered: rss, cache, unevictable, active_file, inactive_file, mapped_file, active_anon, inactive_anon, shmem.
Memory types considered: locked, page cache, mmap file, anonymous, stack, tmpfs.
Simplified version (no shared memory involved)
Full version (with shared memory)